Distributed file system (DFS) service optimized for IDE usage
General purpose file system lacks of key features required for next generation Cloud IDE
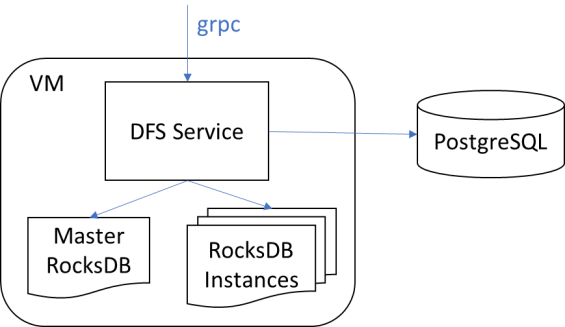
Distributed file system (DFS) service optimized for IDE usage is required to be (as any DFS service) scalable and highly-available. Typical DFS service (like Apache HDFS) or Cloud Object Storage (like Amazon S3) is optimized for streaming large binary objects while providing weak consistency guaranties. Unlike most of such services, DFS optimized for IDE usage should deal with not only objects (files) and their contents, but with their layout (directory structure) as well. Files layout and corresponding files contents represent a working copy of a project which should be strongly consistent. Those consistent sets of files are called DFS snapshots. In addition, DFS optimized for IDE usage should be able to represent history of a project files as a partially ordered set of snapshots. DFS optimized for IDE usage should allow to easily retrieve changes between any historical snapshots, since this feature is necessary for different IDE services like compilers, parsers, indexers, builders of project/code models, etc. Ability to retrieve changes results in optimal storing strategy when only changes between successive snapshots can be stored in underlying cloud services.
In short, DFS optimized for IDE usage should provide unique features:
- access to file system layouts (directory structures);
- consistent snapshot of file system, its layout and files contents;
- immutable history of file system; branches;
- working with changes; optimal storing.
Immutable file system snapshots
Directory structure and files contents are accessible as immutable consistent snapshots of data. Distributed file system stores only changed files between neighbour snapshots. Snapshots are ready-to-use for immediate switching to.
Non-linear history
Immutable snapshots are organized in a non-linear history with branching which doesn’t certainly reflect external branching. Distributed file system can build history tree suitable for its own needs in order to provide better user experience, e.g., during population of huge git repos.
Content de-deduplication
Distributed file system supports content de-duplication out of the box. Same contents of different files even in different projects do not waste cloud storage space. De-duplication lets detecting unchanged files even if they are claimed as changed.
Custom metadata storage
Distributed file system service provides rich tagging API for marking/searching for projects/repos and particular snapshots. One can tag a snapshot with a tag or unique tag, search for a snapshot by tag or by tag prefix.
Snapshot contexts
Distributed file system service allows to define an isolated view on a filesystem in some context. Snapshot contexts can be used to storing auxiliary files (build files, generated files, indices, etc.) related and associated with particular file system snapshot.
Continuous sync with external git repositories
Special git-syncer service creates new file system snapshots associated with git commits.
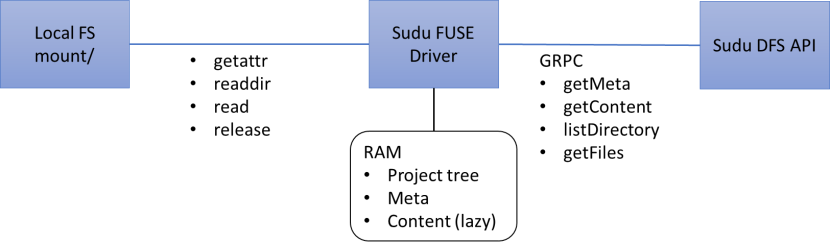
Can be integrated to development workflow via VsCode extension or FUSE driver.